Shadows
In the 3D world, light and shadows have always been extremely important components that enrich the entire environment. High quality shadows can make the game world look more realistic.
Creator 3.0 currently supports two types of shadows, Planar and ShadowMap.
Enabling Shadow Effect
To enable the shadow effect for an object, proceed as follows:
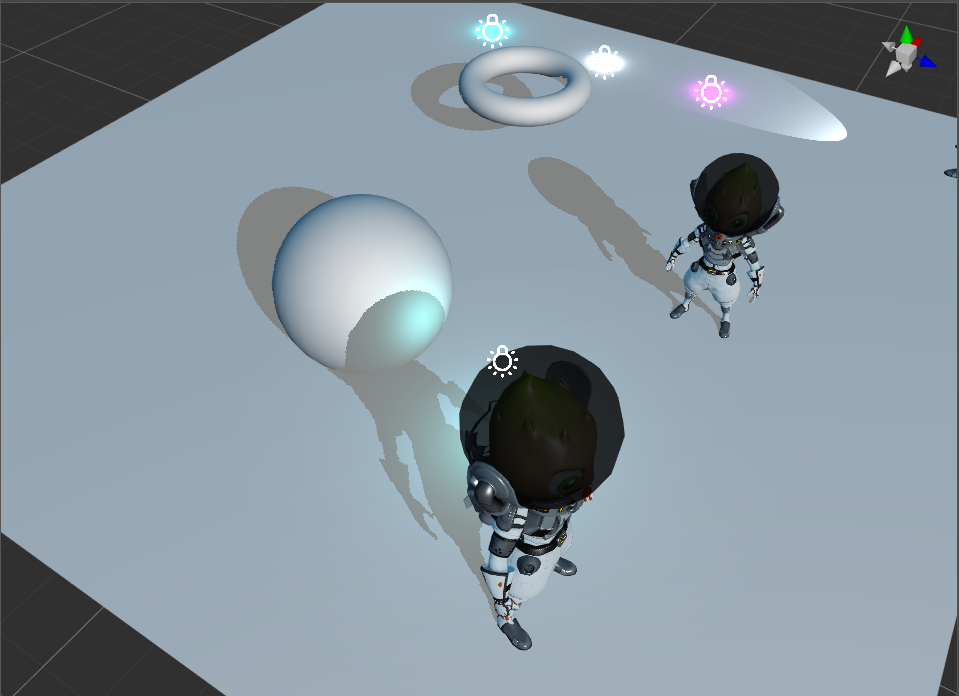
Check Scene in the Hierarchy panel, and then check the Enabled property in the Shadows component of the Inspector panel.
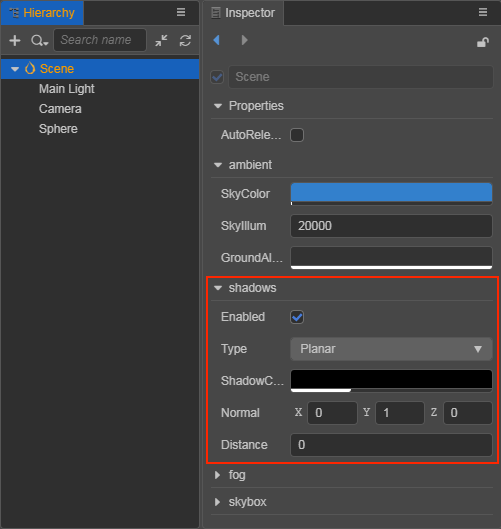
Select the 3D node that needs to display shadows in the Hierarchy panel, and then set the ShadowCastingMode property to ON in the MeshRenderer component of the Inspector panel.
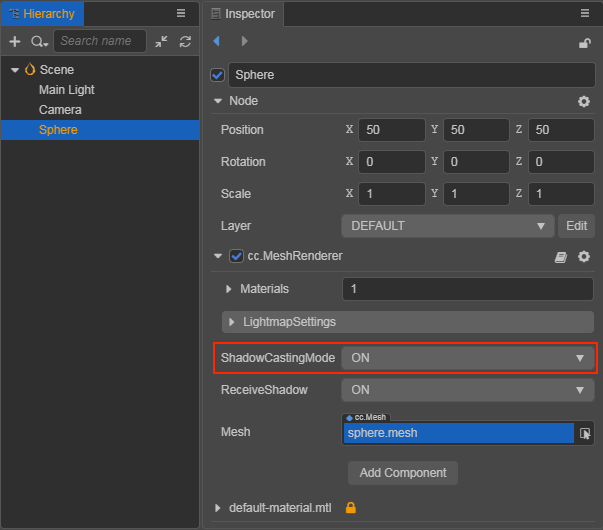
If the type of shadows is ShadowMap, set the ReceiveShadow property on the MeshRenderer component to ON.
Note: if shadows are not displayed properly, adjust the direction of the directional light.
Types of Shadows
The types of shadows can be set in the Type property of the Shadows component.
Planar Shadows
The planar shadows are generally used for simpler scenes.
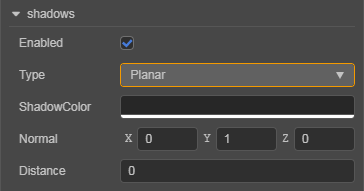
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Enabled | Whether to enable shadow effect. |
| Type | The type of shadows. |
| ShadowColor | The color of shadows. |
| Normal | The normal line perpendicular to shadows, used to adjust the slope of shadows. |
| Distance | The distance between the shadow receiving plane and the origin of the coordinate. |
Adjust the direction of the directional light to adjust the position of shadows.
Note: planar shadows are only cast on planar surfaces, not on objects, which means that the ReceiveShadow property in the MeshRenderer component is invalid.
ShadowMap
ShadowMap renders the scene with the lights as the viewpoint. From the position of the lights, the places in the scene that are not visible are where shadows are created.
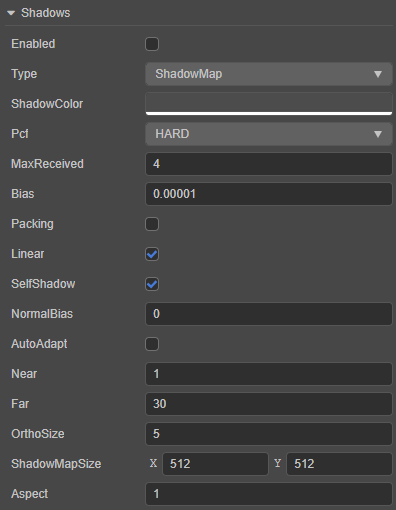
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Enabled | Whether to enable the shadow effect. |
| Type | Choose the shadow type. |
| ShadowColor | Color value of the resulting shadow. |
| Pcf | Set the anti-aliasing level of the shadow edge, currently including HARD, FILTER_X5, FILTER_X9, FILTER_X25. Please refer to the section PCF Soft Shadow below for details. |
| MaxReceived | The maximum number of lights supported for shadow generation, default is 4, can be adjusted as needed. |
| Bias | Set the offset value of shadows to prevent z-fitting. |
| Packing | ShadowMap compression, which can be enabled for some devices that do not support floating point textures. This optimizes performance, but the texture quality is lower (mutually exclusive with the Linear option, only one of the two can be chosen). |
| Linear | Enables linear depth for spotlights only, which can be used to improve the shadow quality of the spotlight (mutually exclusive with Packing option). |
| SelfShadow | Enable the self-shadowing effect for objects in the scene. |
| NormalBias | Set the normal offset value from -1 ~ 1. When SelfShadow is enabled, light leakage on curved surfaces can be resolved by adjusting the value of this option (this option is only displayed when SelfShadow option is checked). |
| AutoAdapt | If checked, the range of shadows will be calculated automatically, as described in section AutoAdapt Adaptive Shadow Calculation below. If this option is unchecked, the following properties are enabled to manually set the range of shadow generation. |
| Near | Set the near clipping plane of the main lights shadow camera. |
| Far | Set the far clipping plane of the main lights shadow camera. |
| OrthoSize | Set the ortho viewport size of the main lights shadow camera. |
| ShadowMapSize | Set the texture size of shadows. |
| Aspect | Set the ortho viewport aspect ratio of the main lights shadow camera. |
ShadowMap receives and displays shadow effects generated by other objects when ReceiveShadow on the object MeshRenderer component is enabled.
ShadowMap is generally used for scenes that require more realistic and complex light and shadow effects. The downside is that if the lights is not moved, then the previously generated ShadowMap can be reused, while once the lights is moved, then a new ShadowMap needs to be recalculated.
PCF Soft Shadow
Percentage Closer Filtering (PCF) is a simple, common technique used to achieve shadow edge desampling, by smoothing shadow edges to eliminate aliasing in shadow mapping. The principle is to sample around the current pixel (also called a fragment), then calculate the ratio of the sample closer to the lights compared to the fragment, use this ratio to scale the scattered light and specular light, and then color the fragment to blur the shadow edges.
Cocos Creator currently supports 5x, 9x, and 25x sampling. The larger the magnification, the larger the sampling area and the more blurred the shadow edges.
AutoAdapt Adaptive Shadow Calculation
AutoAdapt adaptive shadow calculation will automatically calculate the range of shadows created under the lightView, as well as the distance of the shadow camera.
Support dynamic batching to improve performance
For models with instancing enabled in the material, the planar shadows will be drawn using instancing automatically as well. Please refer to the Dynamic Batching documentation for details.