ScrollView Component Reference
ScrollView is a container with a scroll function. It provides a way to browse more contents within a limited display area. Generally, ScrollView will be used along with the Mask component and the ScrollBar component can also be added to show the current offset location within the browsing content.

Click the Add Component button at the bottom of the Inspector panel and select UI/ScrollView to add the ScrollView component to the node.
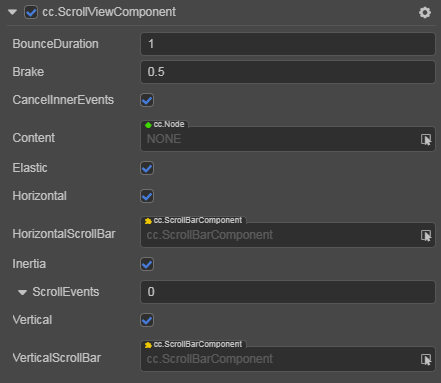
ScrollView Properties
| Properties | Function Explanation |
|---|---|
| BounceDuration | Floating point number, the time duration for bounce back. The value range is 0-10 |
| Brake | Floating point number, the deceleration coefficient after scrolling. The value range is 0-1. If set to 1, then the scrolling will stop immediately, if set to 0, then the scrolling will continue until the content border |
| CancelInnerEvents | If it is set to true, then the scroll behavior will cancel the touch events registered on the child node. The default setting is true |
| Content | A reference node for the inner content of the ScrollView. It could be a node containing a very large image or long texts. |
| Elastic | Boolean value, whether to bounce back or not while scroll to the border. |
| Horizontal | Boolean value, whether horizontal scroll is allowed or not |
| HorizontalScrollBar | A reference node for creating a scroll bar showing the horizontal position of the content |
| Inertia | Is there an accelerating velocity when scrolling |
| ScrollEvents | Default list type is null. Each event added by the user is composed of the node reference, component name and a response function. Please see the ScrollView Event section below for details |
| Vertical | Boolean value, whether vertical scroll is allowed or not |
| VerticalScrollBar | A reference node for creating a scroll bar showing vertical position of the contents |
ScrollView Event
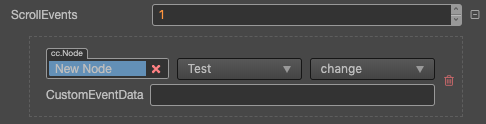
For event structure you can refer to the Button documentation.
The ScrollView event callback will have two parameters, the first one is the ScrollView itself and the second one is the event type of ScrollView.
ScrollBar Setting
ScrollBar is optional. You can choose to set either a Horizontal ScrollBar or a Vertical ScrollBar or of course set them both.
To build a connection, you can drag a node with the ScrollBar component in the Hierarchy over to the corresponding field in ScrollView.
Detailed Explanation
The ScrollView component can only work with the specified content node. It calculates location information during scrolling using both the designated scroll direction and the length of the content node in this direction.
The Content node can also set up the auto resize by adding a WidgetComponent, or it can arrange the layout of child nodes by adding a LayoutComponent, but these two components should not be added to a node at the same time to avoid unintentional consequences.
Normally a ScrollView node tree resembles the following:
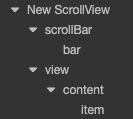
The view here is used to define a scroll area that can be displayed. As a result, the MaskComponent will normally be added to the view. Contents that can scroll can be put in the content node or added to its child node.
Add a callback through the script code
Method one
The event callback added by this method is the same as the event callback added by the editor, all added by code. First you need to construct a EventHandler object, and then set the corresponding target, component, handler and customEventData parameters.
import { _decorator, Component, ScrollViewComponent, EventHandler } from "cc";
const { ccclass, property } = _decorator;
@ccclass("example")
export class example extends Component {
onLoad() {
const scrollViewEventHandler = new EventHandler();
// This node is the node to which your event handler code component belongs
scrollViewEventHandler.target = this.node;
// This is the code file name
scrollViewEventHandler.component = 'example';
scrollViewEventHandler.handler = 'callback';
scrollViewEventHandler.customEventData = 'foobar';
const scrollview = this.node.getComponent(ScrollViewComponent);
scrollview.scrollEvents.push(scrollViewEventHandler);
}
callback(scrollview, eventType, customEventData){
// here scrollview is a Scrollview component object instance
// here the eventType === ScrollViewComponent.EventType enum
// here the customEventData parameter is equal to the "foobar" you set before
}
}
Method two
By scrollview.node.on('scroll-to-top', ...) way to add.
// Suppose we add an event handler callback to the onLoad method of a component and handle the event in the callback function:
import { _decorator, Component, ScrollViewComponent } from "cc";
const { ccclass, property } = _decorator;
@ccclass("example")
export class example extends Component {
@property(ScrollViewComponent)
scrollview: ScrollViewComponent | null = null;
onLoad(){
this.scrollview.node.on('scroll-to-top', this.callback, this);
}
callback(scrollView: ScrollViewComponent){
// The callback parameter is the ScrollView component, note that events registered this way cannot pass customEventData.
}
}
Similarly, you can register events such as scrolling, touch-up, scroll-began, etc. The parameters of the callback function for these events are consistent with the parameters of scroll-to-top.