Render Texture
A render texture is a texture on the GPU. Usually, we set it to the camera's target texture, so that the content illuminated by the camera is drawn to the texture via the frambuffer off the screen. Typically can be used to create car mirrors, implement dynamic shadows, etc.
Creating a RenderTexture
Click the + button in the top left of the Assets panel and select RenderTexture to create a Render Texture:
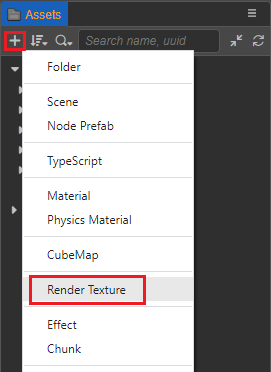
The properties associated with the render texture asset can then be set in the Inspector panel.
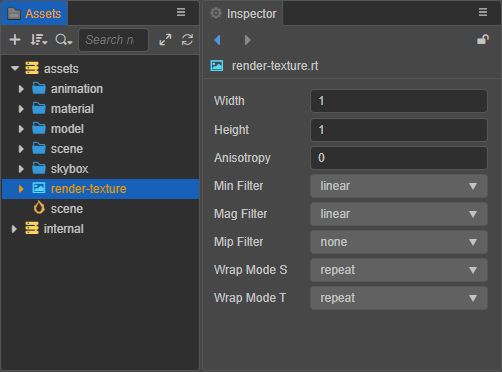
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Width | Set the width of the render texture. |
| Height | Set the height of the render texture. |
| Anisotropy | Anisotropy value. |
| Min Filter | Narrowing filtering algorithm. |
| Mag Filter | Amplification filtering algorithm. |
| Mip Filter | Multi-level texture filtering algorithm. |
| Wrap Mode S | S(U) direction texture addressing mode. |
| Wrap Mode T | T(V) direction texture addressing mode. |
Use RenderTexture in editor
In the camera component, assigning RenderTexture to the camera's TargetTexture property will draw the result of the camera's illumination onto the RenderTexture.
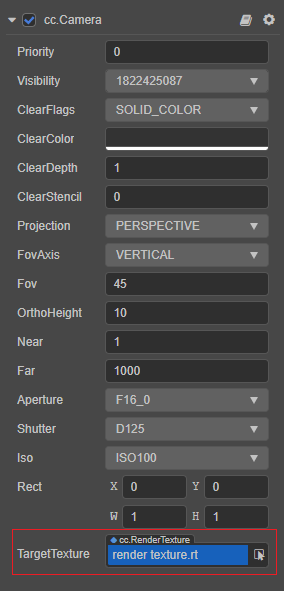
Use RenderTexture in 2D / UI
RenderTexture can be used like a normal texture. Take Sprite Component as an example, drag and drop from Assets panel onto the SpriteFrame property on Sprite's Inspector panel.
![]()
Use RenderTexture in material
To use RenderTexture in material includes the following two steps:
Handle uv in effect asset. Determine
SAMPLE_FROM_RT, and call theCC_HANDLE_RT_SAMPLE_FLIPfunction:#if USE_TEXTURE v_uv = a_texCoord * tilingOffset.xy + tilingOffset.zw; #if SAMPLE_FROM_RT CC_HANDLE_RT_SAMPLE_FLIP(v_uv); #endif #endifSelect the corresponding material in the Assets panel, then check
SAMPLE FROM RTin the Inspector panel: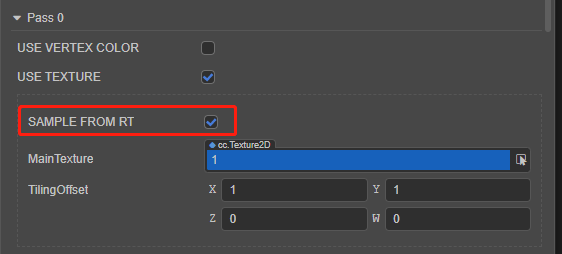
RenderTexture program guide
There are two ways to use RenderTexture programmatically:
Method 1: Draw the contents illuminated by the 3D camera to the sprite frame of the UI.
typescriptimport { _decorator, Component, RenderTexture, SpriteFrame, Sprite, Camera } from 'cc'; const { ccclass, property } = _decorator; @ccclass('CaptureToWeb') export class CaptureToWeb extends Component { @property(Sprite) sprite: Sprite = null; @property(Camera) camera: Camera = null; protected _renderTex: RenderTexture = null; start() { const sp = new SpriteFrame(); const renderTex = this._renderTex = new RenderTexture(); renderTex.reset({ width: 256, height: 256, }); this.camera.targetTexture = renderTex; sp.texture = renderTex; this.sprite.spriteFrame = sp; } }Method 2: Draw the contents illuminated by the 3D camera to the 3D model.
typescriptimport { _decorator, Component, MeshRenderer, RenderTexture, Camera, Material } from 'cc'; const { ccclass, property, requireComponent } = _decorator; @ccclass("RenderCameraToModel") @requireComponent(Camera) export class RenderCameraToModel extends Component { @property(MeshRenderer) model: MeshRenderer = null; start() { const renderTex = new RenderTexture(); renderTex.reset({ width: 256, height: 256, }); const cameraComp = this.getComponent(Camera); cameraComp.targetTexture = renderTex; const pass = this.model.material.passes[0]; // Set the 'SAMPLE_FROM_RT' macro to 'true' so that RenderTexture can be displayed correctly on each platform const defines = { SAMPLE_FROM_RT: true, ...pass.defines }; const renderMat = new Material(); renderMat.initialize({ effectAsset: this.model.material.effectAsset, defines, }); this.model.setMaterial(renderMat, 0); renderMat.setProperty('mainTexture', renderTex, 0); } }Make sure that the shader has a
mainTextureproperty and is enabled in the material if you want to display the drawing results correctly. For example, if using thebuiltin-standardshader, make sure the USE ALBEDO MAP option is checked:
For more information about the usage, please refer to the example RenderTexture.