Raycast Detection
Raycast detection is a very important function and is often used to judge various situations. The essence is to make a intersection judgment between a ray and another shape, as shown in the figure below.
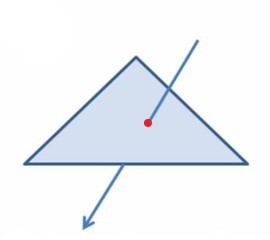
Constructing a Ray
The ray is under the geometry namespace of the cc module, so in order to access to ray, we need to import geometry:
import { geometry } from "cc";
The ray is composed of start point and direction. There are the following common methods to construct a ray:
- Via
start point++direction, such asrayconstructor or static interfacecreate:
import { geometry } from "cc";
const { ray } = geometry;
// Construct a ray starting from (0, -1, 0) and pointing to the Y axis
// The first three parameters are the starting point, the last three parameters are the direction
const outRay = new ray(0, -1, 0, 0, 1, 0);
// Or through the static method create
const outRay2 = ray.create(0, -1, 0, 0, 1, 0);
- Via
start point+another point on the ray, for example the static interfacefromPointsin theray:
import { geometry, Vec3 } from "cc";
// Construct a ray starting from the origin and pointing to the Z axis
const outRay = new geometry.ray();
geometry.ray.fromPoints(outRay, Vec3.ZERO, Vec3.UNIT_Z);
- Use the camera to construct a ray emitted from the origin of the camera to a point on the screen (or the near plane of the camera):
Note: First you need to get a reference to a camera component or camera instance.
Note: The order of the interface parameters exposed by both the camera component and the camera instance is not the same.
import { geometry, CameraComponent } from "cc";
const { ray } = geometry;
// It is assumed here that there is already a reference to cameraCom
const cameraCom: CameraComponent;
const cameraCom: CameraComponent;
// Get a ray emitted by the screen coordinates (0, 0)
const outRay = new ray();
cameraCom.screenPointToRay(0, 0, outRay);
Interface Introduction
Cocos Creator 3D provides a set of ray detection functions based on the physics engine in the v1.0.1 version.
However, it should be noted that the detected object is a physics collider, and the corresponding collider component on the inspector panel, such as BoxColliderComponent.
Currently, the interface is provided by PhysicsSystem, which has the following two categories:
raycastAll: Detect all colliders and return a Boolean value to indicate whether the detection was successful.raycastClosest: Detect all colliders and return Boolean value as well.
Parameter explanation:
worldRay: Rays in world spacemask: Mask for filtering, you can pass in the packets to be detectedmaxDistance: Maximum detection distance, please do not pass Infinity or Number.MAX_VALUEqueryTrigger: Whether to detect triggers
Getting Results
To get the detection results of the above interfaces, you need to use the following methods separately:
- Get the detection results of
raycastAll:PhysicsSystem.instance.raycastResults - Get the detection result of
raycastClosest:PhysicsSystem.instance.raycastClosestResult
Note: The returned object is read-only and reused, and the corresponding result will be updated after each call to the detection interface.
Information Stored By Results
The information is stored by PhysicsRayResult, which mainly has the following information:
collider: Collider that is hitdistance: The distance between the hit point and the starting point of the rayhitPoint: hit point (in world coordinate system)hitNormal:The normal of the hit point's face (in the world coordinate system) (supported inv1.1version, currently there is no such information inbuiltin)
Related test cases can be found here.
Return to the using physics documentation.