Custom Materials for 2D Rendering Objects
Custom materials for 2D rendering objects are a best practice to extend the performance of 2D rendering objects and enhance the capabilities of 2D rendering objects themselves, allowing for cool rendering effects such as dissolve and glow.
Most of the 2D renderable components in v3.0 support the use of custom materials, with the following interface (using the Sprite component as an example).
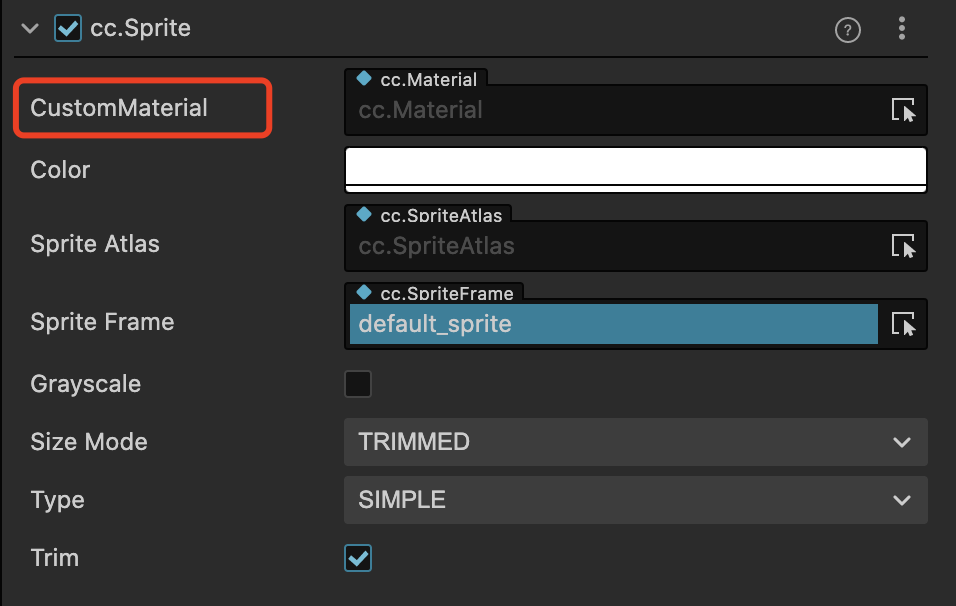
The usage is no different from other built-in materials, just drag and drop the material to be used into the CustomMaterial property box, but there are some points to note as follows:
When no custom material is specified, the built-in material will be used for rendering, please refer to the Sprite Component Reference documentation.
2D rendering objects do not support multiple materials, the maximum number of custom materials is one.
Please use a 2D-specific shader such as builtin-spine or builtin-sprite to customize materials, do not choose a shader used by other 3D components.
The Grayscale property on the panel is disabled when a custom material for 2D rendering objects is used, and the user can choose to implement this feature in the material itself.
If the BlendFactor is set in the code, when a custom material is used, the BlendFactor setting in the custom material will prevail.
When a custom material is used, the depth detection information of the component will be based on the material. To achieve occlusion with 3D objects, please use custom materials and turn on depth detection. See the example 2d-rendering-in-3d.
If you want to change the properties of the custom material, it can be done by getting the customMaterial on the 2D renderer component as following code( take Sprite for example):
tslet spriteComp = this.node.getComponent(Sprite); let material = spriteComp.customMaterial; //material.setProperty(proName,val)
Write your own 2D Shader
If the built-in shaders does not meet the demand, please refer to the 2D Sprite Effect:Gradient to customize the shader.