UI Custom Material
Sprite supports UI Custom Material. The user interface is as follows:
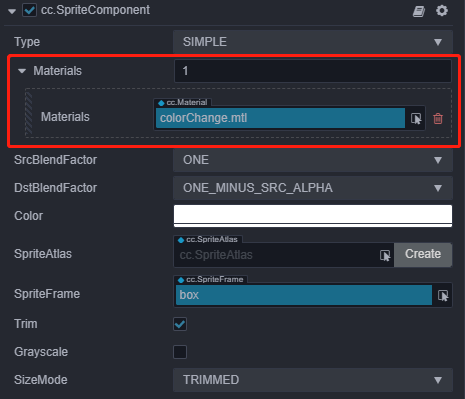
Using a custom material works the same as the UI_built-in materials. However, there are few items to take into consideration:
- When the number of custom materials is set to
0or empty, the default material will be used. Please refer to the Sprite documentation. - UI does not support multiple materials, the number of custom materials is at most one.
- When the ui custom material is used, the
Grayscalefunction on the panel will be invalid. Users can choose to implement this function in the material. - After setting the custom material, the
Colorproperty on the panel will be mixed with the color set in the material itself (if had) to affect the rendering color of the sprite. - For custom materials, developers need to introduce the
cc-sprite-textureheader file in the shader and sample thecc_spriteTexture. Image resources can be directly set and used by the sprite through theSpriteFrameon the settings panel. For example, a simple fragment shader that uses the panel setting
SpriteFrameto sample textures should look like the following:CCProgram sprite-fs %{ precision highp float; #include <embedded-alpha> #include <cc-sprite-texture> // Introduce preset header files in vec4 color; in vec2 uv0; uniform Constant { vec4 mainColor; }; vec4 frag () { vec4 o = vec4(1, 1, 1, 1); o *= texture(cc_spriteTexture, uv0); // sample cc_spriteTexture o *= color; o *= mainColor; return o; } }%To perform uniform assignment operations to custom materials, they can operate by obtaining the material on the Sprite. We provide different interfaces to deal with different operating conditions, as shown in the following code: (Please pay attention to the difference Notes on the interface!)
let spriteCom = this.node.getComponent(Sprite); // What is obtained through the sharedMaterial method is a shared material resource, and operations on material will affect all rendering objects that use this material let material = spriteCom.sharedMaterial; // The material trial used by the current rendering component obtained through the material method, the operation for material Instance will only affect the current component let materialInstance = spriteCom.material;