进阶篇 - 添加阴影、光照和动画
在本节中我们将向您介绍如何完善 快速上手:制作第一个游戏 中制作的原型,如何使用第三方资源比如动画资源等等。
光照和阴影
光影是描述游戏的重要渲染特性,通过光源和阴影,我们可以模拟更加真实的游戏世界,提供更好的沉浸感和代入感。
接下来我们为角色加上简单的影子。
开启阴影
在 层级管理器 中点击最顶部的
Scene节点,然后在 属性检查器 勾选shadows中的 Enabled,并修改 Distance 和 Normal 属性: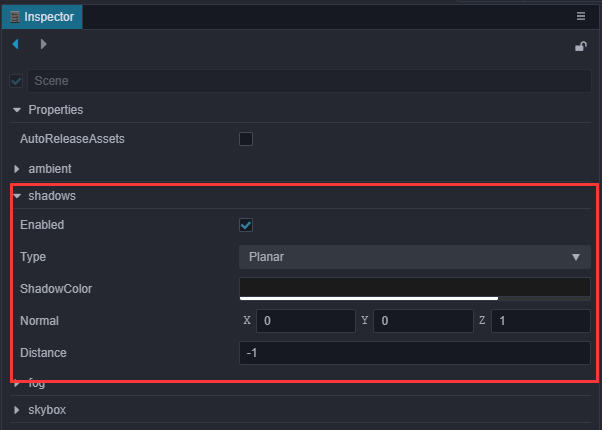
点击 Player 节点下的 Body 节点,将
cc.MeshRenderer组件中的 ShadowCastingMode 设置为 ON。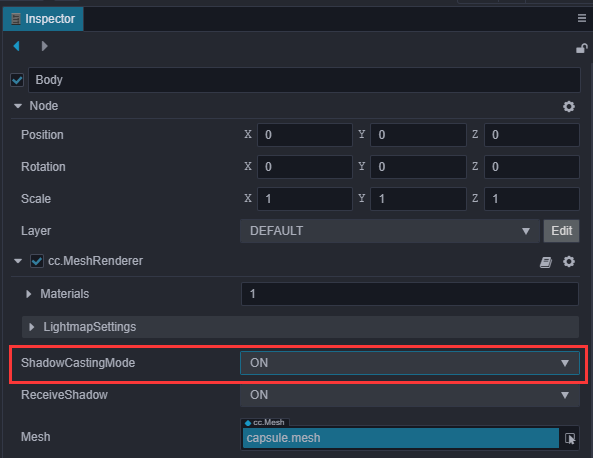
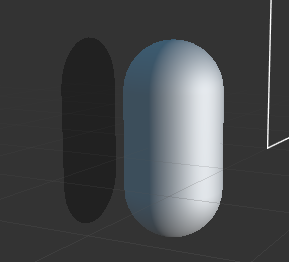
此时在 场景编辑器 中会看到一个阴影面片,预览会发现看不到这个阴影,这是因为它在模型的正后方,被胶囊体盖住了。
调整光照
新建场景时默认会添加一个挂载了 cc.DirectionalLight 组件的 Main Light 节点,由这个平行光计算阴影。所以为了让阴影换个位置显示,我们可以调整这个平行光的方向。在 层级管理器 中点击选中 Main Light 节点,调整 Rotation 属性为(-10,17,0)。
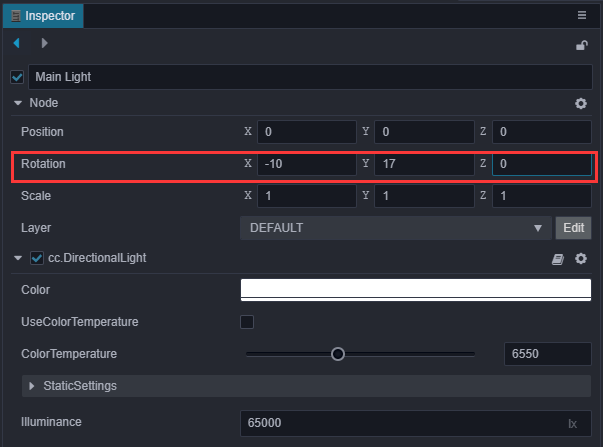
点击预览可以看到影子效果:

添加主角模型
做为一个官方教程,用胶囊体当主角显的有点寒碜,所以我们花(低)重(预)金(算)制作了一个 Cocos 主角。
导入模型资源
从原始资源导入模型、材质、动画等资源不是本篇基础教程的重点,所以这边直接使用已经导入工程的资源。将 项目工程(GitHub | Gitee)中 assets 目录下的 cocos 文件夹拷贝到你自己工程的 assets 目录下。
添加到场景中
在 cocos 文件中已经包含了一个名为 Cocos 的 Prefab,将它拖拽到 层级管理器 中 Player 节点下的 Body 节点中,作为 Body 节点的子节点。
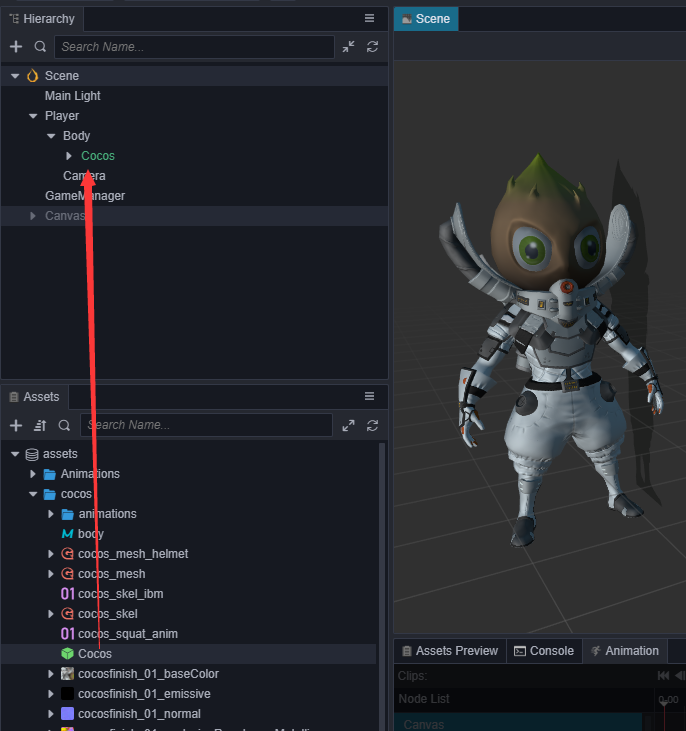
同时在 属性检查器 中移除原先的胶囊体模型:
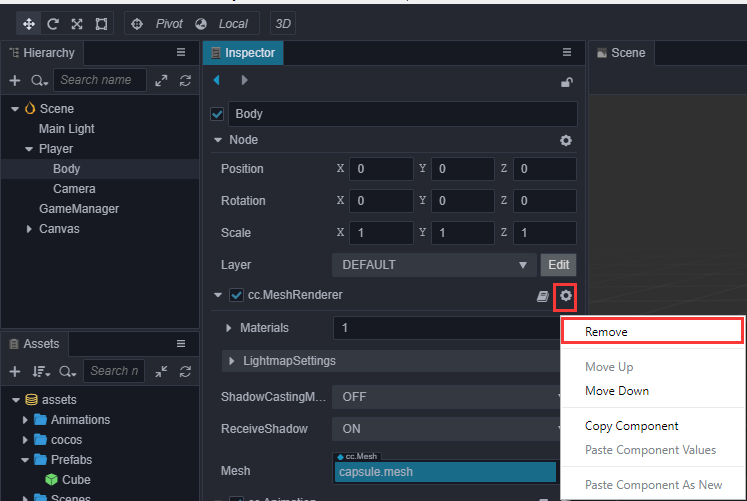
此时会发现模型有些暗,可以在 Cocos 节点下加个聚光灯(Spotlight),以突出它锃光瓦亮的脑门。
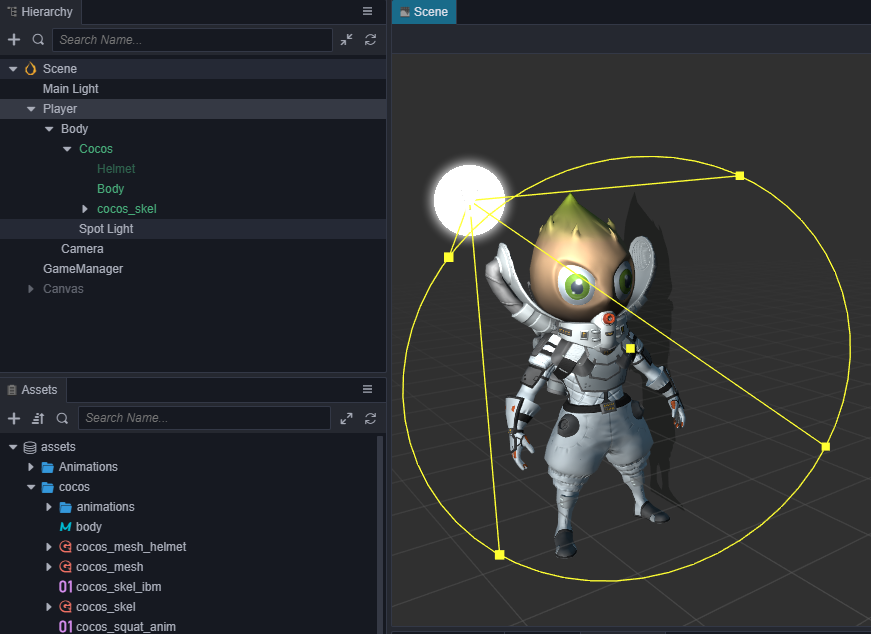
添加跳跃动画
现在预览可以看到主角初始会有一个待机动画,但是跳跃时还是用这个待机动画会显得很不协调,所以我们可以在跳跃过程中将其换成跳跃的动画。在 PlayerController.ts 类中添加一个引用模型动画的变量:
@property({type: SkeletalAnimation})
public CocosAnim: SkeletalAnimation|null = null;同时,因为我们将主角从胶囊体换成了人物模型,可以弃用之前为胶囊体制作的动画,并注释相关代码:
// @property({type: Animation})
// public BodyAnim: Animation|null = null;
jumpByStep(step: number) {
// ...
// if (this.BodyAnim) {
// if (step === 1) {
// this.BodyAnim.play('oneStep');
// } else if (step === 2) {
// this.BodyAnim.play('twoStep');
// }
// }
}然后在 层级管理器 中将 Cocos 节点拖拽到 Player 节点的 CocosAnim 属性框中:
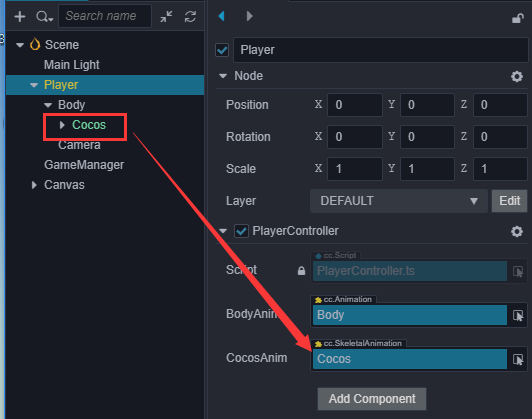
在 PlayerController 脚本的 jumpByStep 函数中播放跳跃动画:
jumpByStep(step: number) {
if (this._startJump) {
return;
}
this._startJump = true;
this._jumpStep = step;
this._curJumpTime = 0;
this._curJumpSpeed = this._jumpStep / this._jumpTime;
this.node.getPosition(this._curPos);
Vec3.add(this._targetPos, this._curPos, new Vec3(this._jumpStep, 0, 0));
if (this.CocosAnim) {
this.CocosAnim.getState('cocos_anim_jump').speed = 3.5; // 跳跃动画时间比较长,这里加速播放
this.CocosAnim.play('cocos_anim_jump'); // 播放跳跃动画
}
// if (this.BodyAnim) {
// if (step === 1) {
// this.BodyAnim.play('oneStep');
// } else if (step === 2) {
// this.BodyAnim.play('twoStep');
// }
// }
this._curMoveIndex += step;
}这里 _jumpStep 时间是 0.3 秒,如果动画播放的时长和 _jumpStep 不匹配可能会导致如下问题:
- 动画还没播放完毕,出现动画过渡不平滑
- 或者动画播放完毕但跳跃时间还没有到产生滑步现象
一种处理方法使我们直接通过动画剪辑的时长和 _jumpStep 来计算重新计算动画的速度而不是使用常量:
var state = this.CocosAnim.getState('cocos_anim_jump');
state.speed = state.duration/this._jumpTime;开发者可以自行尝试,或者手动修改 _jumpStep 和 speed 到合适的值以控制游戏的节奏。
在 PlayerController 脚本的 onOnceJumpEnd 函数中让主角变为待机状态,播放待机动画。
onOnceJumpEnd() {
if (this.CocosAnim) {
this.CocosAnim.play('cocos_anim_idle');
}
this.node.emit('JumpEnd', this._curMoveIndex);
}注意:当跳跃完成时会触发
onOnceJumpEnd,详情请见PlayerController.ts中的update函数实现。
预览效果如下:

最终代码
PlayerController.ts
import { _decorator, Component, Vec3, input, Input, EventMouse, Animation, SkeletalAnimation } from 'cc';
const { ccclass, property } = _decorator;
@ccclass("PlayerController")
export class PlayerController extends Component {
@property({type: Animation})
public BodyAnim: Animation|null = null;
@property({type: SkeletalAnimation})
public CocosAnim: SkeletalAnimation|null = null;
// for fake tween
private _startJump: boolean = false;
private _jumpStep: number = 0;
private _curJumpTime: number = 0;
private _jumpTime: number = 0.3;
private _curJumpSpeed: number = 0;
private _curPos: Vec3 = new Vec3();
private _deltaPos: Vec3 = new Vec3(0, 0, 0);
private _targetPos: Vec3 = new Vec3();
private _curMoveIndex = 0;
start () {
}
reset() {
this._curMoveIndex = 0;
}
setInputActive(active: boolean) {
if (active) {
input.on(Input.EventType.MOUSE_UP, this.onMouseUp, this);
} else {
input.off(Input.EventType.MOUSE_UP, this.onMouseUp, this);
}
}
onMouseUp(event: EventMouse) {
if (event.getButton() === 0) {
this.jumpByStep(1);
} else if (event.getButton() === 2) {
this.jumpByStep(2);
}
}
jumpByStep(step: number) {
if (this._startJump) {
return;
}
this._startJump = true;
this._jumpStep = step;
this._curJumpTime = 0;
this._curJumpSpeed = this._jumpStep / this._jumpTime;
this.node.getPosition(this._curPos);
Vec3.add(this._targetPos, this._curPos, new Vec3(this._jumpStep, 0, 0));
if (this.CocosAnim) {
this.CocosAnim.getState('cocos_anim_jump').speed = 3.5; //跳跃动画时间比较长,这里加速播放
this.CocosAnim.play('cocos_anim_jump'); //播放跳跃动画
}
// if (this.BodyAnim) {
// if (step === 1) {
// this.BodyAnim.play('oneStep');
// } else if (step === 2) {
// this.BodyAnim.play('twoStep');
// }
// }
this._curMoveIndex += step;
}
onOnceJumpEnd() {
if (this.CocosAnim) {
this.CocosAnim.play('cocos_anim_idle');
}
this.node.emit('JumpEnd', this._curMoveIndex);
}
update (deltaTime: number) {
if (this._startJump) {
this._curJumpTime += deltaTime;
if (this._curJumpTime > this._jumpTime) {
// end
this.node.setPosition(this._targetPos);
this._startJump = false;
this.onOnceJumpEnd();
} else {
// tween
this.node.getPosition(this._curPos);
this._deltaPos.x = this._curJumpSpeed * deltaTime;
Vec3.add(this._curPos, this._curPos, this._deltaPos);
this.node.setPosition(this._curPos);
}
}
}
}GameManager.ts
import { _decorator, Component, Prefab, instantiate, Node, Label, CCInteger, Vec3 } from 'cc';
import { PlayerController } from "./PlayerController";
const { ccclass, property } = _decorator;
// 赛道格子类型,坑(BT_NONE)或者实路(BT_STONE)
enum BlockType{
BT_NONE,
BT_STONE,
};
enum GameState{
GS_INIT,
GS_PLAYING,
GS_END,
};
@ccclass("GameManager")
export class GameManager extends Component {
// 赛道预制
@property({type: Prefab})
public cubePrfb: Prefab | null = null;
// 赛道长度
@property({type: CCInteger})
public roadLength: Number = 50;
private _road: BlockType[] = [];
// 主界面根节点
@property({type: Node})
public startMenu: Node | null = null;
// 关联 Player 节点身上 PlayerController 组件
@property({type: PlayerController})
public playerCtrl: PlayerController | null = null;
// 关联步长文本组件
@property({type: Label})
public stepsLabel: Label | null = null!;
start () {
this.curState = GameState.GS_INIT;
this.playerCtrl?.node.on('JumpEnd', this.onPlayerJumpEnd, this);
}
init() {
// 激活主界面
if (this.startMenu) {
this.startMenu.active = true;
}
// 生成赛道
this.generateRoad();
if(this.playerCtrl){
// 禁止接收用户操作人物移动指令
this.playerCtrl.setInputActive(false);
// 重置人物位置
this.playerCtrl.node.setPosition(Vec3.ZERO);
// 重置已经移动的步长数据
this.playerCtrl.reset();
}
}
set curState (value: GameState) {
switch(value) {
case GameState.GS_INIT:
this.init();
break;
case GameState.GS_PLAYING:
if (this.startMenu) {
this.startMenu.active = false;
}
if (this.stepsLabel) {
this.stepsLabel.string = '0'; // 将步数重置为0
}
// 会出现的现象就是,游戏开始的瞬间人物已经开始移动
// 因此,这里需要做延迟处理
setTimeout(() => {
if (this.playerCtrl) {
this.playerCtrl.setInputActive(true);
}
}, 0.1);
break;
case GameState.GS_END:
break;
}
}
generateRoad() {
// 防止游戏重新开始时,赛道还是旧的赛道
// 因此,需要移除旧赛道,清除旧赛道数据
this.node.removeAllChildren();
this._road = [];
// 确保游戏运行时,人物一定站在实路上
this._road.push(BlockType.BT_STONE);
// 确定好每一格赛道类型
for (let i = 1; i < this.roadLength; i++) {
// 如果上一格赛道是坑,那么这一格一定不能为坑
if (this._road[i-1] === BlockType.BT_NONE) {
this._road.push(BlockType.BT_STONE);
} else {
this._road.push(Math.floor(Math.random() * 2));
}
}
// 根据赛道类型生成赛道
let linkedBlocks = 0;
for (let j = 0; j < this._road.length; j++) {
if(this._road[j]) {
++linkedBlocks;
}
if(this._road[j] == 0) {
if(linkedBlocks > 0) {
this.spawnBlockByCount(j - 1, linkedBlocks);
linkedBlocks = 0;
}
}
if(this._road.length == j + 1) {
if(linkedBlocks > 0) {
this.spawnBlockByCount(j, linkedBlocks);
linkedBlocks = 0;
}
}
}
}
spawnBlockByCount(lastPos: number, count: number) {
let block: Node|null = this.spawnBlockByType(BlockType.BT_STONE);
if(block) {
this.node.addChild(block);
block?.setScale(count, 1, 1);
block?.setPosition(lastPos - (count - 1) * 0.5, -1.5, 0);
}
}
spawnBlockByType(type: BlockType) {
if (!this.cubePrfb) {
return null;
}
let block: Node|null = null;
switch(type) {
case BlockType.BT_STONE:
block = instantiate(this.cubePrfb);
break;
}
return block;
}
onStartButtonClicked() {
// 点击主界面 play 按钮,开始游戏
this.curState = GameState.GS_PLAYING;
}
checkResult(moveIndex: number) {
if (moveIndex < this.roadLength) {
// 跳到了坑上
if (this._road[moveIndex] == BlockType.BT_NONE) {
this.curState = GameState.GS_INIT;
}
} else { // 跳过了最大长度
this.curState = GameState.GS_INIT;
}
}
onPlayerJumpEnd(moveIndex: number) {
if (this.stepsLabel) {
// 因为在最后一步可能出现步伐大的跳跃,但是此时无论跳跃是步伐大还是步伐小都不应该多增加分数
this.stepsLabel.string = '' + (moveIndex >= this.roadLength ? this.roadLength : moveIndex);
}
// 检查当前下落道路的类型,获取结果
this.checkResult(moveIndex);
}
// update (deltaTime: number) {
// // Your update function goes here.
// }
}总结
恭喜您完成了用 Cocos Creator 制作的第一个游戏!在 GitHub | Gitee 可以下载完整的工程,希望这篇快速入门教程能帮助您了解 Cocos Creator 游戏开发流程中的基本概念和工作流程。如果您对编写和学习脚本编程不感兴趣,也可以直接从完成版的项目工程中把写好的脚本复制过来使用。
接下来您还可以继续完善游戏的各方各面,以下是一些推荐的改进方向:
- 为游戏增加难度,当角色在原地停留1秒就算失败
- 改为无限跑道,动态的删除已经跑过的跑道,延长后面的跑道。
- 增加游戏音效
- 为游戏增加结束菜单界面,统计玩家跳跃步数和所花的时间
- 用更漂亮的资源替换角色和跑道
- 可以增加一些可拾取物品来引导玩家“犯错”
- 添加一些粒子特效,例如角色运动时的拖尾、落地时的灰尘
- 为触屏设备加入两个操作按钮来代替鼠标左右键操作
此外如果希望将完成的游戏发布到服务器上分享给好友玩耍,可以阅读 发布工作流 一节的内容。