WebSocket Server
Developers can launch a WebSocket Server during the game and provide an RPC interface. By improving and calling these RPC interface, developers can monitor the internal state of the game process and increase the ability to manage the game process state.
How To Enable
WebSocket Server is culled by default. You need to set the USE_WEBSOCKET_SERVER = 1 to enable it. There are two ways to enable it.
Method 1: Enable on all platforms —— modify default values
In ccConfig.h, set USE_WEBSOCKET_SERVER to 1.
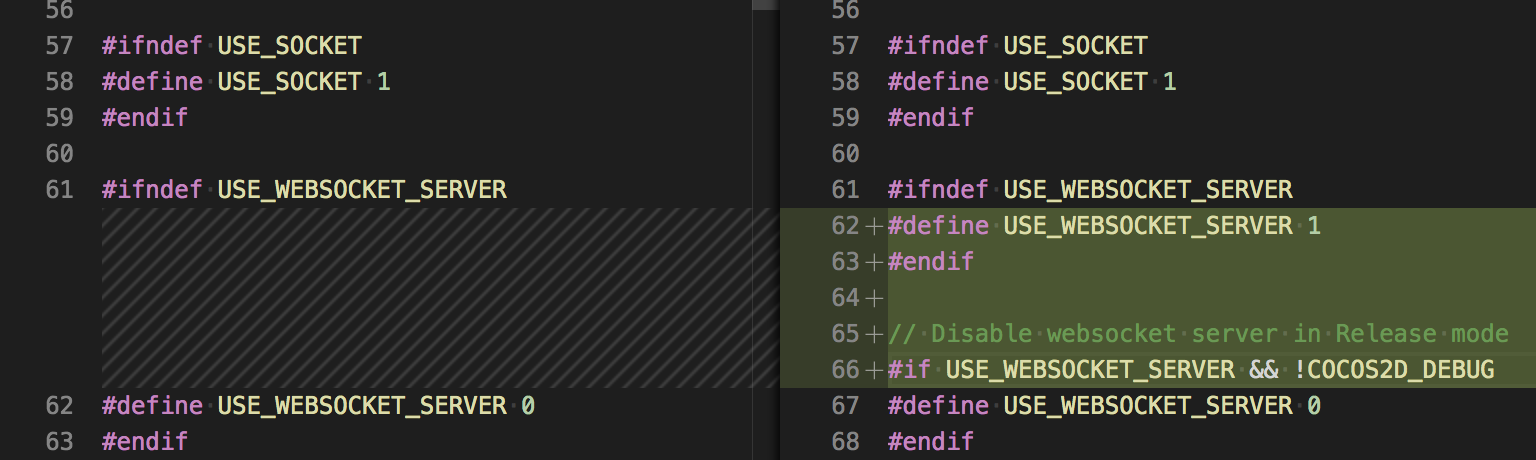
Note: since it is rare to keep the WebSocket Server in Release mode, it is recommended to include the following in the modification:
c++#if USE_WEBSOCKET_SERVER && !COCOS2D_DEBUG #define USE_WEBSOCKET_SERVER 0 #endif
Modifying the default value will affect all platforms. If you don't know whether you need to enable it on all platforms, you can refer to the following method 2, and only enable it for specific platforms.
Method 2: Enable on a specific platform
In some cases, only specific platforms need to enabled the WebSocket Server. You need to set USE_WEBSOCKET_SERVER in different ways.
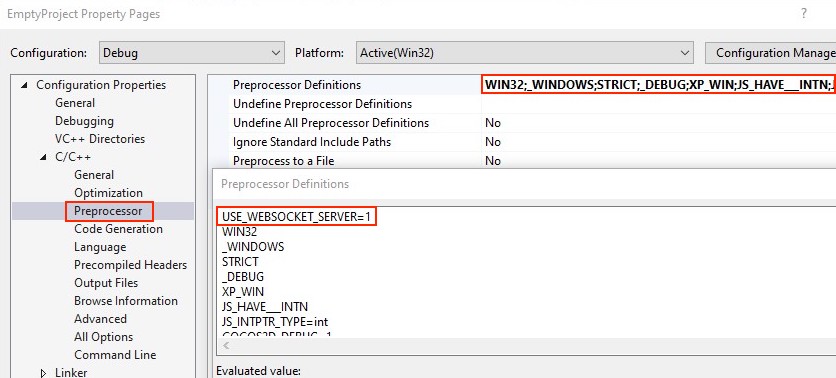
Visual Studio
Editing project properties as shown below:
Android
Editing
proj.android-studio/app/jni/Application.mkas shown below: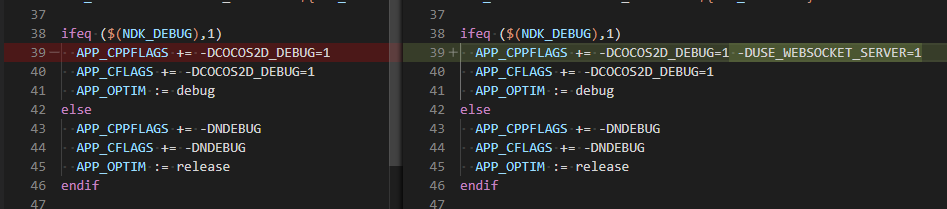
Xcode
Editing project properties as shown below:
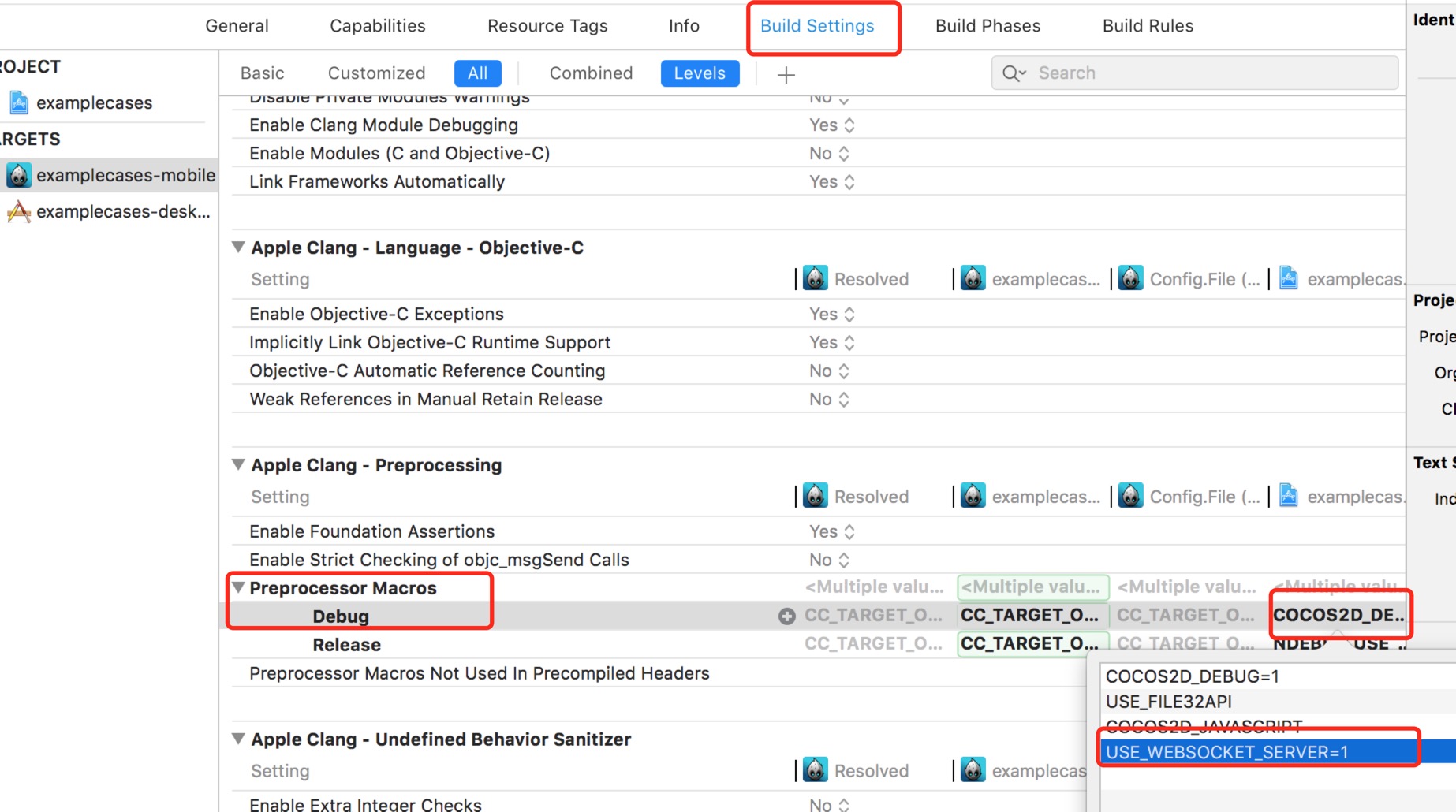
Only through the above configuration can WebSocketSever be called in JS code.
How to use WebSocket
Refer to the example code below:
// In the native platform's Release mode or in Web / WeChat mini games and other platforms, WebSocketServer may not be defined
if (typeof WebSocketServer == "undefined") {
console.error("WebSocketServer is not enabled!");
return;
}
let s = new WebSocketServer();
s.onconnection = function (conn) {
conn.ondata = function (data) {
conn.send(data, (err) => {});
}
conn.onclose = function () {
console.log("connection gone!");
};
};
s.onclose = function () {
console.log("server is closed!");
}
s.listen(8080, (err) => {
if (!err);
console.log("server booted!");
});API
The interface is defined as follows
/**
* Server object
*/
class WebSocketServer {
/**
* Close the server
*/
close(cb?: WsCallback): void;
/**
* Listen and launch the service
*/
listen(port: number, cb?: WsCallback): void;
/**
* Handle new requests
*/
set onconnection(cb: (client: WebSocketServerConnection) => void);
/**
* Set up the server shutdown callback
*/
set onclose(cb: WsCallback);
/**
* Gets all the connection objects
*/
get connections(): WebSocketServerConnection[];
}
/**
* The client connection object in the server
*/
class WebSocketServerConnection {
/**
* Close the connection
*/
close(cb?: WsCallback): void;
/**
* Send the data
*/
send(data: string|ArrayBuffer, cb?: WsCallback): void;
set ontext(cb: (data: string) => void);
set onbinary(cb: (data: ArrayBuffer) => void);
set ondata(cb: (data: string|ArrayBuffer) => void);
set onconnect(cb: () => void;);
set onclose(cb: WsCallback);
set onerror(cb: WsCallback);
get readyState(): number;
}
interface WsCallback {
(err?: string): void;
}Reference links
- The interface design refers to the nodejs-websocket.